🌟“Am I Optimally Nourishing My Body?”
You’re sitting at your meal and suddenly a thought occurs to you:
“Is that truly what my body needs right now?” You strive for a balanced, healthy diet – but can you be sure that your body is currently receiving all the essential nutrients to be vital and efficient all around?
This article addresses exactly that:
You will gain well-founded knowledge about which nutrients are particularly important for your body, in which foods they are found, and how you can integrate this knowledge practically, structured, and time-saving into your daily life – without complicated meal plans or expensive trend products.
Use this guide as a helpful roadmap to specifically and easily ensure that your entire family is optimally supplied with all necessary nutrients in everyday life.
🍏 Nutrients – Understanding the Basis of a Healthy Diet
Planning varied meals for yourself or your family is often challenging. Not only taste and time play a crucial role, but above all, ensuring that meals contain all necessary nutrients – tailored to the individual needs of adults, children, women, and men at different stages of life.
But how exactly do you achieve a balanced diet that includes all important vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, and fats? Which nutrients do children need during their growth phase? Why do women and men sometimes have different dietary requirements? And how does nutrient demand change throughout life?
In this article, you will receive well-founded basic knowledge to better understand nutrients, integrate them specifically into your daily life, and sustainably improve your meal planning. Step by step, you will learn what to pay attention to, which food groups contain which important nutrients, and how to optimally combine them for different family members.
📎which Nutrients Does your Body Really Need?
Your body relies on a variety of nutrients daily to function optimally. These can be divided into the following main groups:
Macronutrients – the energy providers:
- Carbohydrates: The primary energy source for the brain and muscles. Complex carbohydrates from whole grains, vegetables, and fruits are particularly valuable, as they provide the body with long-term energy and keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle building, cell regeneration, and a healthy immune system. Good protein sources include fish, lean meat, legumes, eggs, dairy products, as well as nuts and seeds.
- Fats: Important for cell membranes, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). Healthy fat sources include avocado, fatty fish (e.g., salmon), nuts, seeds, and high-quality vegetable oils such as olive and flaxseed oil.
Micronutrients – small helpers, big impact:
- Vitamins: They play central roles in energy production, the immune system, and cell protection. Particularly important vitamins include:
- B vitamins (e.g., B6, B12, folic acid): indispensable for nerve function, energy metabolism, and cell division.
- Vitamin C: strengthens your immune system and improves iron absorption.
- Vitamin D: supports bone health and immune function.
- Minerals and trace elements: These substances play a key role in bone formation, muscle function, and various metabolic processes. Particularly relevant representatives are:
- Calcium: for strong bones and healthy teeth.
- Iron: essential for blood formation and oxygen transport in the body.
- Magnesium: supports muscle function, nerve conduction, and energy metabolism.
- Zinc: strengthens the immune system and promotes healing processes.
Dietary fiber – underestimated everyday heroes:
Dietary fiber are indigestible components of plant-based foods. They promote healthy digestion, support gut flora, stabilize blood sugar levels, and provide a long-lasting feeling of fullness. Dietary fiber are particularly abundant in whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits.
Water – the indispensable foundation:
Water is crucial for almost every metabolic process. It regulates body temperature, supports nutrient transport, and ensures efficient waste product excretion. A daily intake of at least 1.5 to 2 liters is recommended, with more depending on physical activity and external conditions.
📎Compact Nutrient Table: which Nutrient is Contained where?
Here’s an overview 👉
Nutrient Needs of Women and Men – Important Differences
Although everyone needs the same basic nutrients, the amounts differ depending on age, gender, life stage, and individual needs. Especially between men and women, there are significant differences in daily nutrient requirements.
📎Women – What should be Paid Special Attention to?
The female body places different demands on nutrition depending on the stage of life. In the following table, you will find a compact overview of the nutrient needs of women per life stage.
Nutrient needs of women – differentiated by life stages:
Here’s an overview 👉
🌸 Special Additions: Nutrients for Women in Focus
- ♀️ Cycle Health & Energy (Iron, Magnesium, Vitamin B12, omega-3 fatty acids)
Iron and Vitamin B12 help with regular menstruation and ensure stable energy levels. Magnesium supports muscle relaxation and omega-3 fatty acids support emotional balance. - 🦴 Bone Health (Calcium, Vitamin D, Magnesium)
Especially from the age of 30, calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium are essential to maintain bone mass long-term and prevent osteoporosis. - ❤️ Heart Health (omega-3 fatty acids, Magnesium, Vitamin B12)
Women particularly benefit from omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and vitamin B12, which strengthen and protect the cardiovascular system. - 🤰 Pregnancy & Lactation (Folic Acid, omega-3 fatty acids, Iron, Vitamin D, Calcium)
These nutrients support healthy baby development and ensure optimal maternal nutrition during and after pregnancy. - 💪 Muscle Maintenance & Vitality (Protein, Vitamin B12, Magnesium)
Especially important from 50 years: Sufficient protein intake and Vitamin B12 help build and maintain muscle, which improves long-term quality of life. - 🧠 Mental Health & Stress Reduction (omega-3 fatty acids, Magnesium, B-Vitamins)
omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and B vitamins help women better cope with emotional stress and hormonal fluctuations.
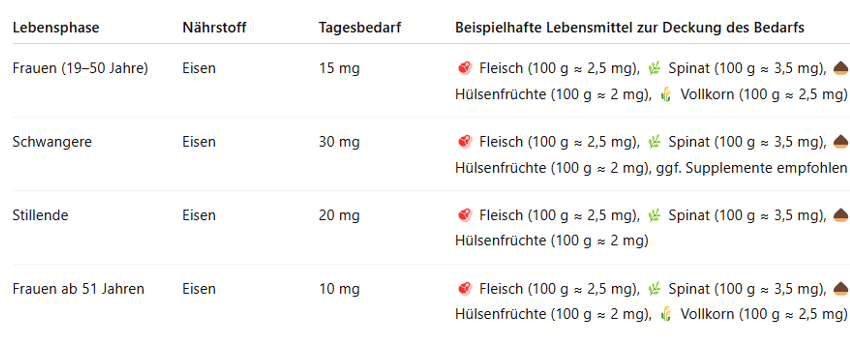
🥦 Iron – Central Role
Iron plays a central role in oxygen transport in the body and is crucial for energy production, mental performance, and immune defense. Women, in particular, have an increased need due to monthly bleeding, during pregnancy and lactation, and with physical activity. A deficiency can cause fatigue, concentration problems, and reduced performance.
The following table clearly shows you how high your iron requirement is depending on your life stage and which foods you can easily use to cover it:
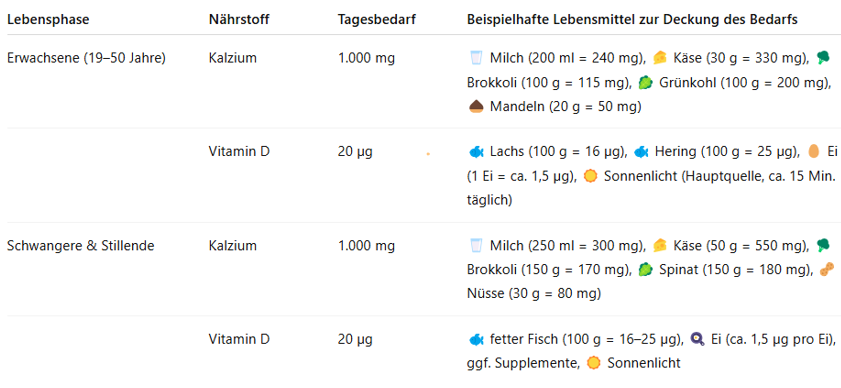
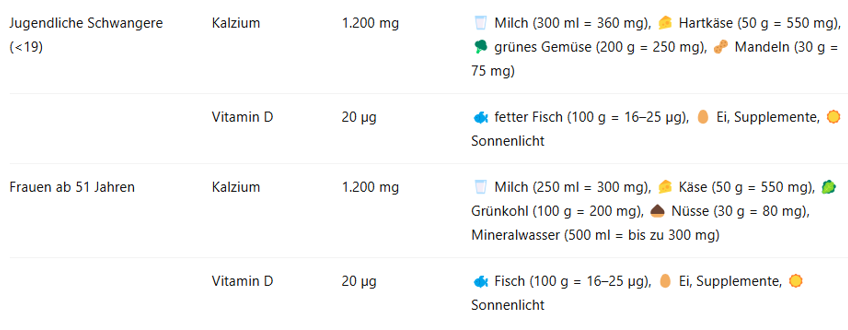
Calcium & Vitamin D – why are They Particularly Important?
Calcium is an essential mineral that plays a significant role in the building and maintenance of healthy bones and teeth. In addition, calcium plays an important role in muscle contraction, blood clotting, and nerve function. A long-term calcium deficiency can lead to osteoporosis (bone loss), especially in women.
Vitamin D supports the body in absorbing calcium from food and thus ensures optimal utilization. In addition, vitamin D is involved in many metabolic processes, strengthens the immune system, and positively influences psychological health. Endogenous formation primarily occurs through sufficient exposure to sunlight outdoors.
The recommended daily intake of calcium and vitamin D varies depending on the life stage. In the following table, you will find a clear overview of the recommended amounts and how you can specifically cover them through your diet:
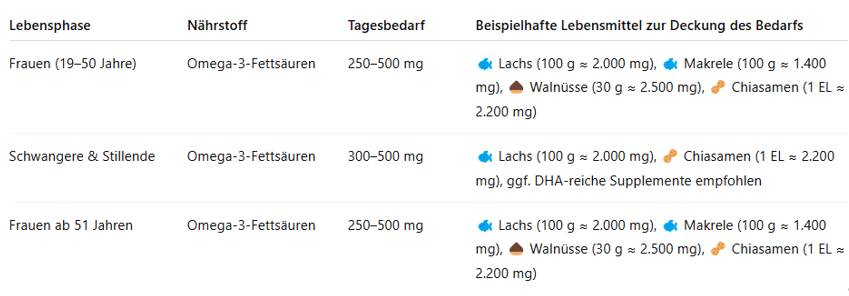
🐟 Omega-3 Fatty Acids
omega-3 fatty acids are healthy fats that your body cannot produce on its own. They are essential for brain function, heart health, hormone regulation, and have anti-inflammatory effects. Women, in particular, benefit from sufficient intake – for example, for healthy skin, stable mood, and during pregnancy for the baby’s brain development.
In the following table, you will learn the recommended daily requirement and which foods are particularly valuable sources of omega-3 fatty acids:
🥬 Folic Acid – Cell Division and Growth
Folic acid is an essential B vitamin, particularly indispensable for cell division and growth. Especially during pregnancy and when trying to conceive, folic acid plays a crucial role in preventing birth defects in the unborn child. Even outside these phases, it is important for blood formation and a healthy nervous system.
This table illustrates the folic acid requirements for different life stages and provides practical tips on which foods are rich in it:

Source:
The reference values provided are based on the current recommendations of the German Nutrition Society (DGE) and the Austrian Nutrition Society (ÖGE). These serve as general guidance. Individual needs may vary.
📎Men – which Nutrients are Particularly Relevant?
Men should also specifically consider certain nutrients in their meals to stay healthy in the long term:
Nutrient needs of men – differentiated by life stages:
Here’s an overview 👉
⭐ Special Additions: Nutrients for Men in Focus
- 💪 Muscle Maintenance:
Protein intake is particularly crucial in older age to counteract muscle loss. - 🧬 Fertility:
Especially important from 30 to 50: Zinc and selenium support sperm production and quality. - ⚡ Energy & Vitality:
Iron, magnesium, and vitamin B12 support long-term energy supply and physical activity. - ❤️ Heart Health:
omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and protein are essential for preventing cardiovascular diseases.
💪 Proteins
Proteins are particularly essential for men, as they significantly influence muscle building, muscle maintenance, and hormone production (especially testosterone). They also play a crucial role in the immune system, recovery after sports activities, and a healthy body composition.
The following table provides a clear overview of the recommended protein intake for different life stages and shows you which foods can easily help you meet it:

🌰 Zinc
Zinc is a crucial trace element, particularly important for men due to its positive effects on fertility, immune system, testosterone production, and skin and hair quality. A deficiency can weaken the immune system and impair physical performance.
The following table will help you meet your daily zinc requirement:

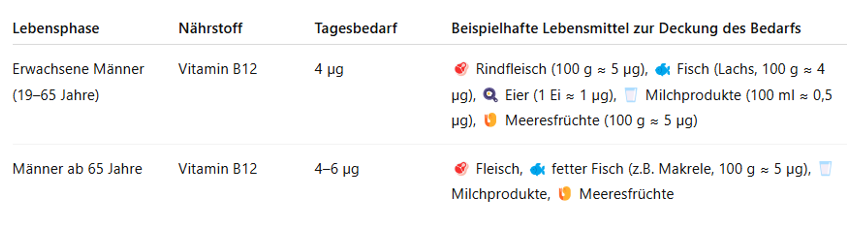
🍳 Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin for men, especially for the nervous system, blood formation, and energy production. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to fatigue, concentration problems, and reduced physical performance.
The table shows you how you can easily meet your daily vitamin B12 requirement:
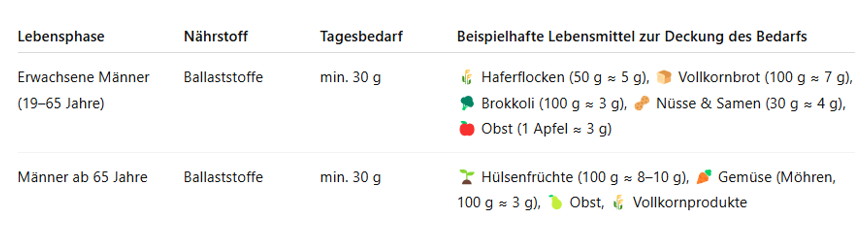
🥗 Dietary Fiber & 🍒 Antioxidants – Double Cell Protection for Men
Dietary fiber promote healthy digestion, regulate blood sugar levels, and support a healthy body weight in the long term. They also nourish the gut flora, which is enormously important for the immune system and hormone balance.
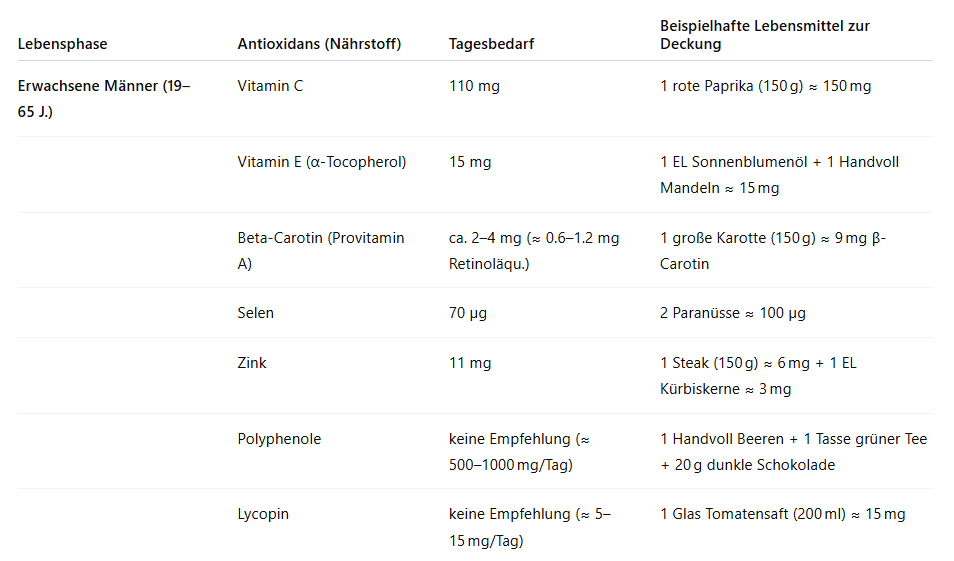
Antioxidants, on the other hand, are the cell-protecting counterparts to free radicals. They neutralize oxidative stress, reduce silent inflammation, and prevent age-related diseases such as heart attack, diabetes, or prostate problems. Especially for men over 40, antioxidant nutrients are essential to prevent cell aging, performance decline, and chronic inflammation.
🧠 Vitamin C, E, zinc, selenium, and plant compounds like beta-carotene, polyphenols, and lycopene form a strong team against oxidative damage – and simultaneously support skin, eyes, nerves, blood vessels, immune defense, and even fertility.
👉 This table illustrates how you can meet your daily requirement: Dietary fiber
👉 This table illustrates how you can meet your daily requirement: Antioxidants
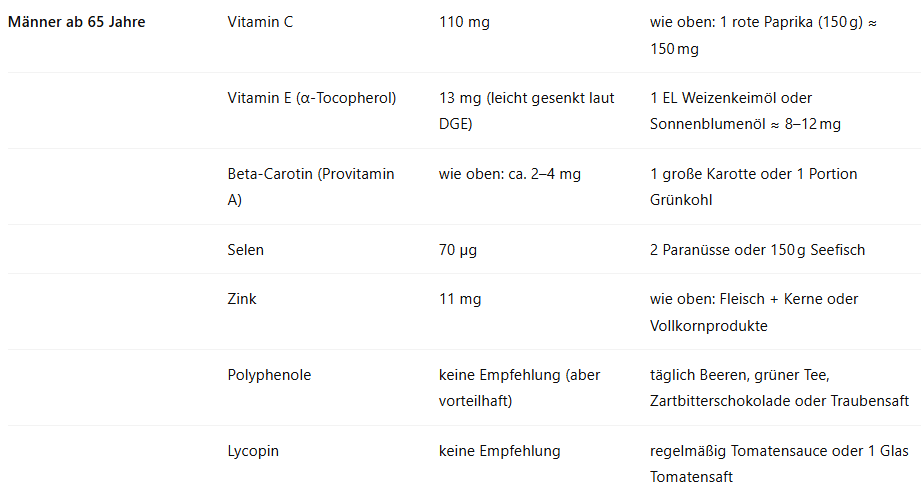
🧠 Tip: Men aged 65 and over particularly benefit from antioxidants such as vitamins C, E, selenium, and polyphenols – they help reduce inflammation, strengthen the immune system, and slow down cell aging.
Source:
The reference values provided are based on the current recommendations of the German Nutrition Society (DGE) and the Austrian Nutrition Society (ÖGE). These serve as general guidance. Individual needs may vary.
Practical Example: how to Apply this New Knowledge Specifically in Weekly Planning
Small Step-By-Step Guide
Step 1: Create a Table for your Family
Create a simple, clear table (e.g., landscape format, or use the enclosed version as a Word or PDF file):
Example:
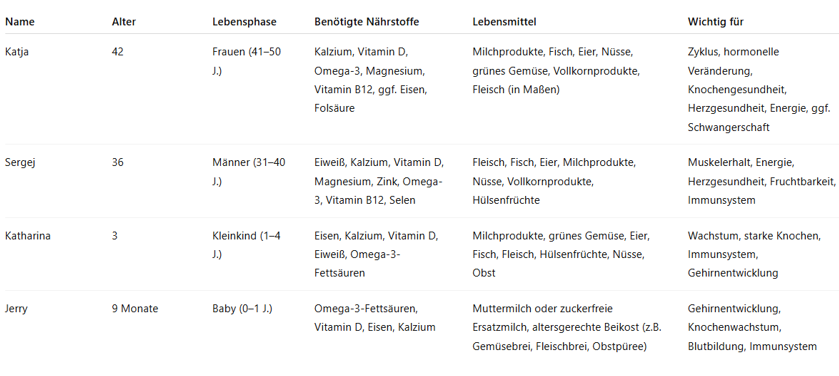
Step 2: Highlight Common Foods
Mark foods that are mentioned multiple times (like eggs, fish, dairy products, vegetables). These will form the focus of your meal planning.
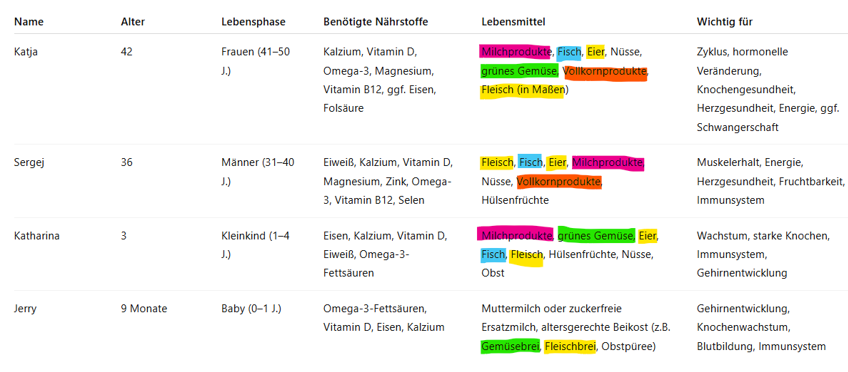
🟢 Commonalities in foods (mark for easy planning):
- 🥚 Eggs
- 🥦 Green vegetables
- 🐟 Fish
- 🥛 Dairy products
- 🥜 Nuts (from approx. 1 year, possible finely chopped or as butter)
- 🍞 Whole grain products (good from 1 year, possible in small amounts adapted for babies)
- 🥩 Lean meat (important iron source, good for everyone)
👶 Extra tip for Jerry (9 months):
- Focus on age-appropriate, finely pureed food or soft pieces.
- Purees with vegetables (e.g., carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin) and small amounts of meat or fish (good source of iron).
- Fruit puree or pureed fruits as a source of vitamins.
Step 3: Derive Specific Meals for your Family
Use the previously marked foods to develop suitable meals for your entire family. Pay special attention to ensuring all needs are considered: adults, toddlers, and babies.
🍽️ Example Meals:


Step 4: Create a Weekly Plan for the Whole Family
Based on these meals, you can now specifically create your weekly plan. Consider the following points:
- Plan meals individually but cohesively: Choose dishes that you can easily adapt for each family member (spices, texture, portion size).
- Plan to save time: Cook once and then adjust the consistency and seasoning for Katharina and Jerry accordingly.
- Balance between variety and routine:
- Choose 2–3 main dishes per week that you can use multiple times.
- Vary side dishes, fruits, and vegetables for variety.
- Plan sensible snack times for energy and nutrients.
K.B. Kitchen Assistant Kati
🍽️ Your smart everyday helper: “Kati” makes nutrient planning easy!
Do you feel overwhelmed by the abundance of information? Don’t worry – with my digital kitchen assistant “Kati”, implementation is effortless. Kati automatically creates individual weekly plans, considers your personal nutrient needs, and prepares practical shopping lists for you.
👉 Test “Kati” now and make your everyday life relaxed, healthy, and full of ease!
Legal Notice & Sources
Note: The information contained in this article serves as guidance and is based on current scientific sources. It does not replace individual nutritional advice or medical care.
📚 References:
Smollich, Martin (2020): The Nutrient Compass – The Book for Competent Handling of Micronutrients. Gräfe und Unzer Verlag, Munich. ISBN 978-3-8338-9580-7.
Kujath, Pauline; Smollich, Martin (2021): Optimal Nutrition Before and During Pregnancy – The Practical Guide. Trias Verlag (Thieme Group), Stuttgart. ISBN 978-3-432-11667-9.
Kersting, Mathilde; Heseker, Helmut (2019): Nutrition Practice – Women and Men: Healthy Eating, Individual Advice. Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart. ISBN 978-3-8252-5116-1.
Reference Values Nutrient Daily Requirement
The stated reference values are based on the current recommendations of the German Nutrition Society (DGE) and the Austrian Nutrition Society (ÖGE). These serve as general guidance. Individual needs may vary.


